What’s the difference between LCD and OLED displays?
Estimated reading time: 7 minutes

There are two main competing display technologies in the market today: LCD and OLED. The mature and dominant technology is the Liquid Crystal Display (LCD), while the up-and-coming challenger is the Organic Light Emitting Diode Display (OLED display). The main difference between LCD and OLED displays is how they create the light and the colors of the image being displayed. This leads to application dependent strengths and weaknesses of either technology.
How do OLED displays work?
OLEDs operate via a solid-state technology, where the individual pixels can emit light in various colors and intensity without the need for an additional light source or color filter. The light-emitting portion of an OLED display is comprised of multiple layers of very specific organic semiconductor materials which can be adjusted to emit light in specific wavelengths. These organic layers have a typical thickness in the order of 100nm. In addition, no backlight is required, allowing for a very thin display module.
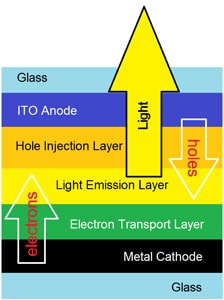
The organic layers beginning on the cathode side of the device consist of several electron transport layers, a recombination layer and end with a hole transport layer on the anode side. The electron transport layers in the OLED stack-up allow movement of electrons from the cathode toward holes supplied from the anode. The electrons and holes recombine in the emissive recombination layer of the film stack-up. This recombination relaxes the energy levels of the electrons, which produces an emission of light. The wavelength of the emitted light is dependent on the chemical composition of the organic materials used in the recombination layer. The intensity of the light is controlled by the amount of current flowing through the OLED’s organic layers. In OLEDs, the individual pixels can emit red, green, or blue light, or – alternatively – they emit white light, which must then pass through color filters.
There are two main varieties of OLED screens: active-matrix and passive-matrix. The difference lies in how the pixels are generated. In the passive-matrix version, each pixel is created by the intersection of two wires, through which electrical current is passed to create a different color. In an active-matrix setup, each pixel has its individual transistor, which allows for faster refresh times and creates smoother motion and transitions in the picture.
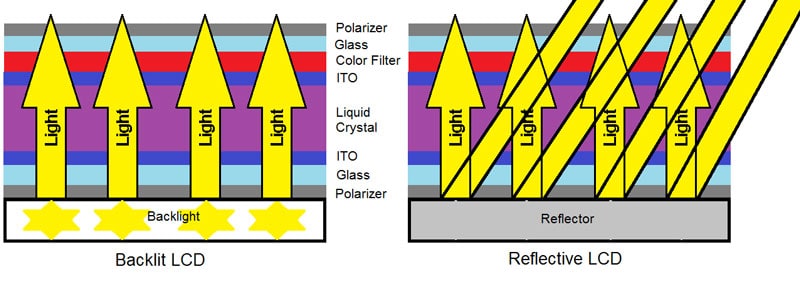
How do LCD displays work?
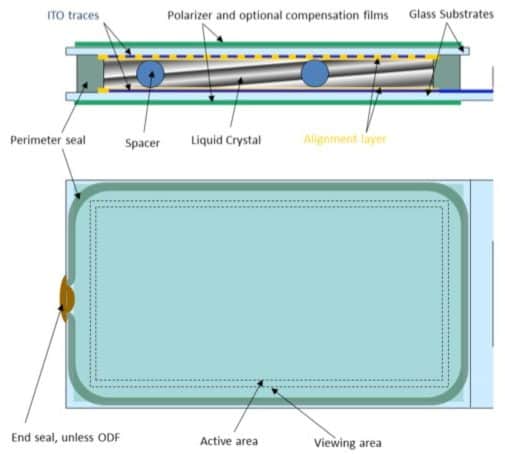
In LCD display technology, the individual pixels modulate light. An applied voltage changes the orientation of liquid crystal molecules that – in conjunction with a pair of polarizers – function as a light shutter by either blocking or allowing light to pass through. LCD displays, therefore, require an additional light source, either from reflected ambient light or more commonly from a “backlight” (an array of LEDs arranged behind or next to the LCD panel). LCD color can be created by adding color filters to the individual pixels. Because OLED displays don’t require the additional backlight, polarizers, or color filter components of an LCD module, they can be made much thinner than LCD displays of equivalent size and resolution.
OLED Display Advantages
OLED display technology can offer power-saving advantages over LCDs, which is important, especially for battery-powered applications such as mobile phones. An OLED’s power consumption will vary with image content and brightness, as light is generated only at the individual pixels needed to display the image. A dark image or a graphic on a black background will consume much less power than bright images or graphics. In contrast, LCD backlights must be ON while the display operates. It’s possible to control individual zones of the backlight separately to save power, but this added complexity is usually only applied in larger displays.
OLEDs can achieve a much higher contrast ratio if reflections from the front surface are carefully controlled. If no current flows through an OLED pixel, it does not emit any light. In contrast the shutter effect of an LCD pixel does not block 100% of the light. Depending on the specific LCD technology used and the angle of observation, a small percentage of the light generated in the backlight can escape. This can wash out dark areas of an image. It is possible but expensive to limit this light leakage to a point where the contrast of an LCD and OLED display become perceptually equivalent.
RGB OLEDs naturally generate a narrow bandwidth of light. This leads to very saturated primary colors and a wide color gamut. This enables OLED technology to display colors which are not easily accessible to LCDs unless RGB backlights or quantum dots are used. Often OLED colors are used “as is”, however, for very high image color fidelity, such high color saturation needs to be electronically ‘tuned down’, to match the color bandwidth of the rendering chain.
LCD Advantages
LCDs offer an advantage over OLEDs in applications where a continuous static image is required. The light emitting materials in OLEDs are affected by luminance decay as a function of the total amount of current that has passed through the pixel. This decay differs for red, green and blue. The dimming effect is subtle, but when adjacent pixels are illuminated at the same time it can become noticeable as an undesired brightness variation or color shift. LCDs don’t suffer from this dimming effect, which makes them a more suitable solution for applications with static images or images with static elements.
Another advantage of LCD technology is the wide variety of different variations to choose from. Depending on the application certain trade-offs can be very attractive. An example is much lower cost for a laptop display compared to a tablet. This is achieved by allowing poor image performance when viewed from the direction the is usually blocked by the keyboard. In a tablet where good viewing performance is required from any direction, much higher cost LCDs or OLEDs must be used.
OLED Display Applications
OLEDs offer an excellent solution for a variety of applications: Glucometers, thermometers, fitness trackers, professional audio equipment, Wi-Fi hotspots, radar detectors, dive computers, biometric transaction devices, and military communications equipment.
They can be used to replace old TN LCDs or add dynamic push buttons on industrial equipment. They can be customized to various resolutions, FPC configurations, colors, custom shaped OLED displays (e.g. octagonal, round, etc.) and can even be made into flexible and transparent displays. Thanks to their versatility, OLED display panel suppliers can offer some exciting capabilities for their customers – things that were previously impossible with LCDs.
As an experienced LCD and OLED panel supplier, New Vision Display can help you find the right technology for your application. Contact us via the below form to discuss your project.