TFT LCD Driver ICs and Interfaces
Estimated reading time: 4 minutes
Table of contents
TFT LCDs have become the norm for small-to-medium size displays in a variety of products within industrial, medical, POS and consumer applications. Compared to passive-addressed monochrome LCDs, TFT displays offer higher contrast, wider viewing angles, faster response time and full color. And, TFT LCDs are now on cost parity with similar size passive LCD displays.
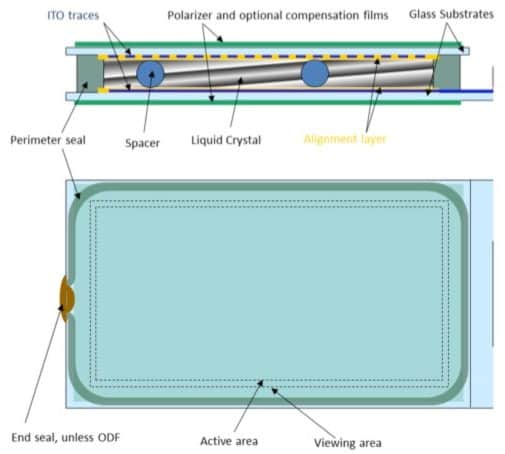
A typical TFT LCD module product consists of a TFT LCD panel, one or more COG (chip-on-glass) driver ICs, a backlight unit, and an interface FPC. Several TFT display interface technologies coexist today. Picking the right technology depends on specific end-product concerns. Most often the display panel input will dictate that choice since TFT panels are designed to be COG bonding pad compatible with a very limited number of driver ICs. This article discusses the interfaces between TFT LCD modules and the typical CPUs found in embedded applications.
TFT Interface Applications
Typical TFT interfaces are determined by the particular TFT panel size and resolution, as shown in the below table. HDMI and eDP require interface converting boards and generally are not used for small to medium-size TFT LCDs.
| TFT LCD Sizes | Resolutions | Typical Interfaces Used |
|---|---|---|
| Up to 3.5″ | 128×160 to 240×320 | SPI, parallel MPU or RGB |
| 4.3” to 7” | 480×272 to 800×480 | RGB |
| Mobile phones | Over 480×854 | RGB, MIPI or LVDS |
| 7″ and larger | 1024×600 and higher | LVDS or MIPI |
SPI Interface
Only the three SPI signals, a CS, and a reset signal are needed. Drawbacks are the inability to read from the display, only write. Also, the frame rate is low and unsuitable for displaying video or high-resolution images.
MCU Parallel Interface
The LCD controller signals are two types: data signals and control signals. The data signals are connected to the LCD data bus and depend on the LCD color depth (8-bit, 9-bit, 16-bit, 18-bit). The control signals are used to define the operation type (read or write), and whether the operation involves in addressing LCD registers or the display RAM.
RGB Interface
An RGB interface is a special kind of parallel interface. This interface works for displays without a frame buffer. The MCU is responsible for updating the display, by providing both the RGB sub-pixel data (16-bit, 18-bit, 24-bit) and the timing signals (HSYNC, VSYNC, DE, CLK).
LVDS Interface
LVDS interfacing has several benefits for TFT displays. It is much less susceptible to EMI and crosstalk issues, allowing the transmitting device to be located farther from the display. Also, LVDS generally consumes less power, pin counts are lower and there are far fewer worries about signal integrity.
MIPI-DSI Interface
High-speed serial interface commonly used on smartphones and tablets. By standardizing this interface, components may be developed that provide higher performance, lower power, less electromagnetic interference and fewer pins than current devices, while maintaining compatibility across products from multiple vendors.
Modern TFT driver ICs are highly integrated chips combining the source driver, gate driver and timing controller (TCON) – as well as other functional circuits such as memory, power circuit, and image processors – into one single IC die. Some driver ICs support multiple interfaces that are selectable on the module FPC or through initialization code firmware.
Looking for guidance? NVD can help.
As a designer and manufacturer of custom LCD modules, New Vision Display works with customers to select the most appropriate and cost-effective TFT display and electronic interface solution for their particular requirement. New Vision Display has nearly 30 years of industry experience as one of the world’s leading TFT LCD screen manufacturers.